- Best Dent Clinic
- +90 (216) 575 55 77
- +90 850 522 65 34
- info@bestdent.com.tr
CHILD DENTAL HEALTH

CHILD DENTAL HEALTH
For one thing, primary teeth serve as guides for the eruption of permanent (adult) teeth, holding the space into which these new teeth will erupt. The crowns (tops) of the permanent teeth actually push against the roots of the baby teeth, causing them to resorb, or melt away. In this way, the adult teeth can take their proper place.
What's more, your child's primary teeth will be there for most of childhood, helping your child to bite, chew and speak. For the first six or so years, he or she will be relying on primary teeth exclusively to perform these important functions. Until around age 12, your child will have a mix of primary and permanent teeth. You will want to make sure those teeth stay healthy and are lost naturally — when it's time.
Your Child's First Teeth
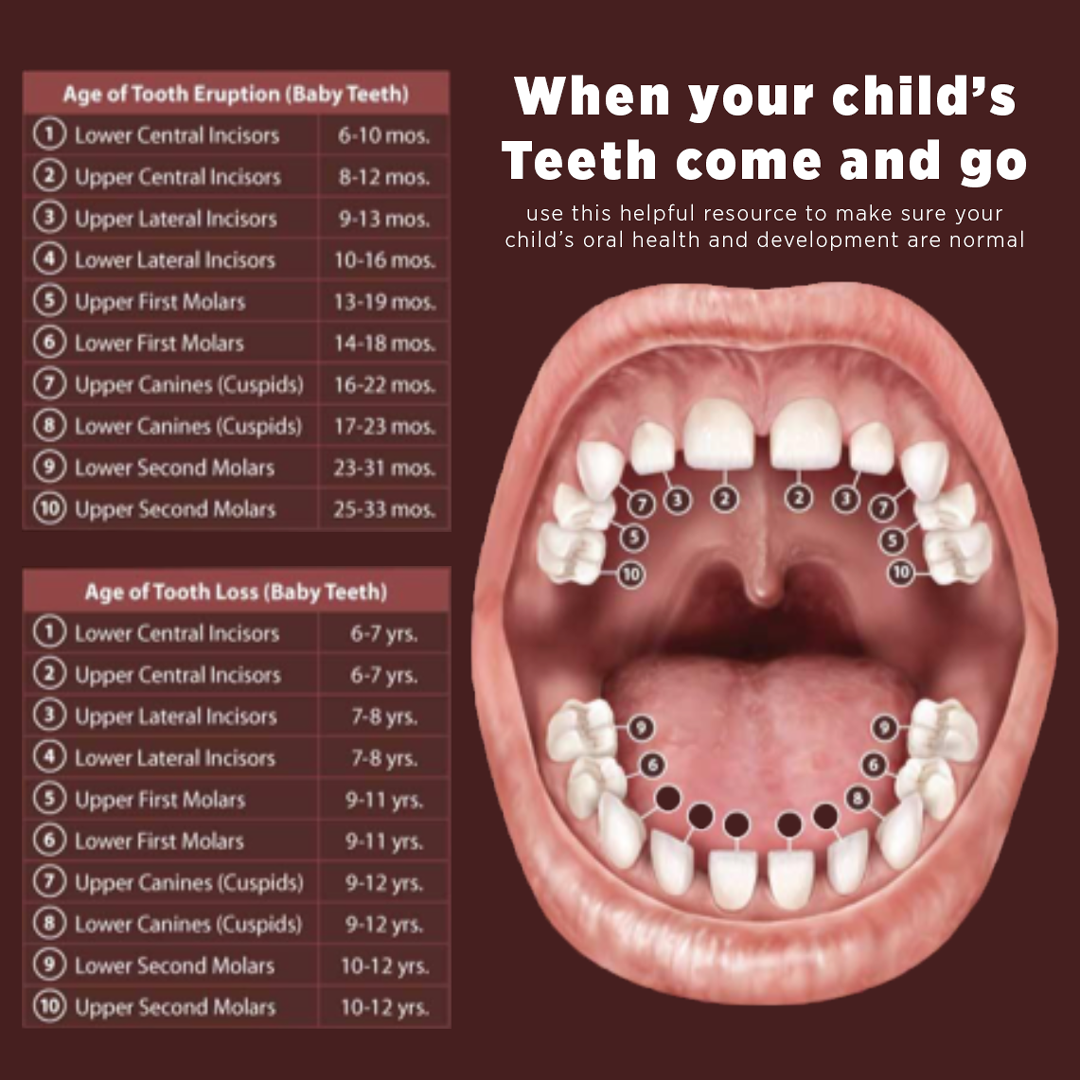
Your child's 20 baby teeth will begin to appear usually between six and nine months, though in some cases it may start as early as three months or as late as twelve months. The two lower front teeth tend to erupt first, followed by the two upper ones. The first molars come in next, followed by the canines (eyeteeth). Sometimes your baby can experience teething discomfort during this process. If so, let us know and we will advise you as to the best course of action.
Your infant's gums and newly erupting teeth should be gently wiped after each feeding with a water-soaked gauze pad or damp washcloth. Any teeth that have fully come in should be cleaned with a small, soft-bristled toothbrush and no more than a thin smear of fluoridated toothpaste. Starting at age 3, you can teach your child to brush with a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste. Your child may need your help with this important task until about the age of 6.
The First Dental Appointment
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that you bring your child in to see us by his/her first birthday. Though this may sound early, we can teach you proper pediatric oral hygiene techniques, check for cavities, and watch for developmental problems
Various forms of tooth decay can affect babies and small children. Early Childhood Caries (tooth decay) can develop rapidly, progressing from the hard, outer enamel layer of a tooth into the softer, inner dentin in six months or less.
Most of all, we want to make sure your child has a positive experience at our office and will be a regular visitor for years to come.

The First Dental Appointment
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that you bring your child in to see us by his/her first birthday. Though this may sound early, we can teach you proper pediatric oral hygiene techniques, check for cavities, and watch for developmental problems
Various forms of tooth decay can affect babies and small children. Early Childhood Caries (tooth decay) can develop rapidly, progressing from the hard, outer enamel layer of a tooth into the softer, inner dentin in six months or less.
Most of all, we want to make sure your child has a positive experience at our office and will be a regular visitor for years to come.
Pediatric Dental Treatments
There are a variety of dental treatments we provide to prevent tooth decay in children, or to save or repair teeth when necessary. They include:
Topical Fluoride — Fluoride incorporates into the enamel of teeth, making it harder and more resistant to decay. Although there is a small amount of fluoride in toothpastes and in some drinking water supplies, we can apply a higher concentration onto your child's teeth for maximum protection
Dental Sealants — We can apply a plastic coating that prevents cavities by sealing the little grooves on the chewing surfaces of back teeth known as “pits and fissures.” These little crevices become the perfect environments for decay-causing bacteria. Immature tooth enamel is more permeable and therefore less resistant to tooth decay. Dental sealants are easy to apply and provide years of protection
Root Canal Treatment — Perhaps you have had a root canal treatment yourself, to save an injured or severely decayed tooth. Well, sometimes children need root canals, too. As mentioned above, baby teeth are important guides to the permanent teeth that are already forming beneath your child's gums. Therefore, saving them from premature loss can help prevent a malocclusion (“mal” – bad; “occlusion” – bite) that requires orthodontic treatment.
Bonding — Chips and minor fractures to front teeth — common childhood occurrences — can be repaired with tooth-colored bonding materials. These lifelike resins made of plastic and glass can be used on baby teeth as well as permanent teeth and last until the youngster has completed facial growth
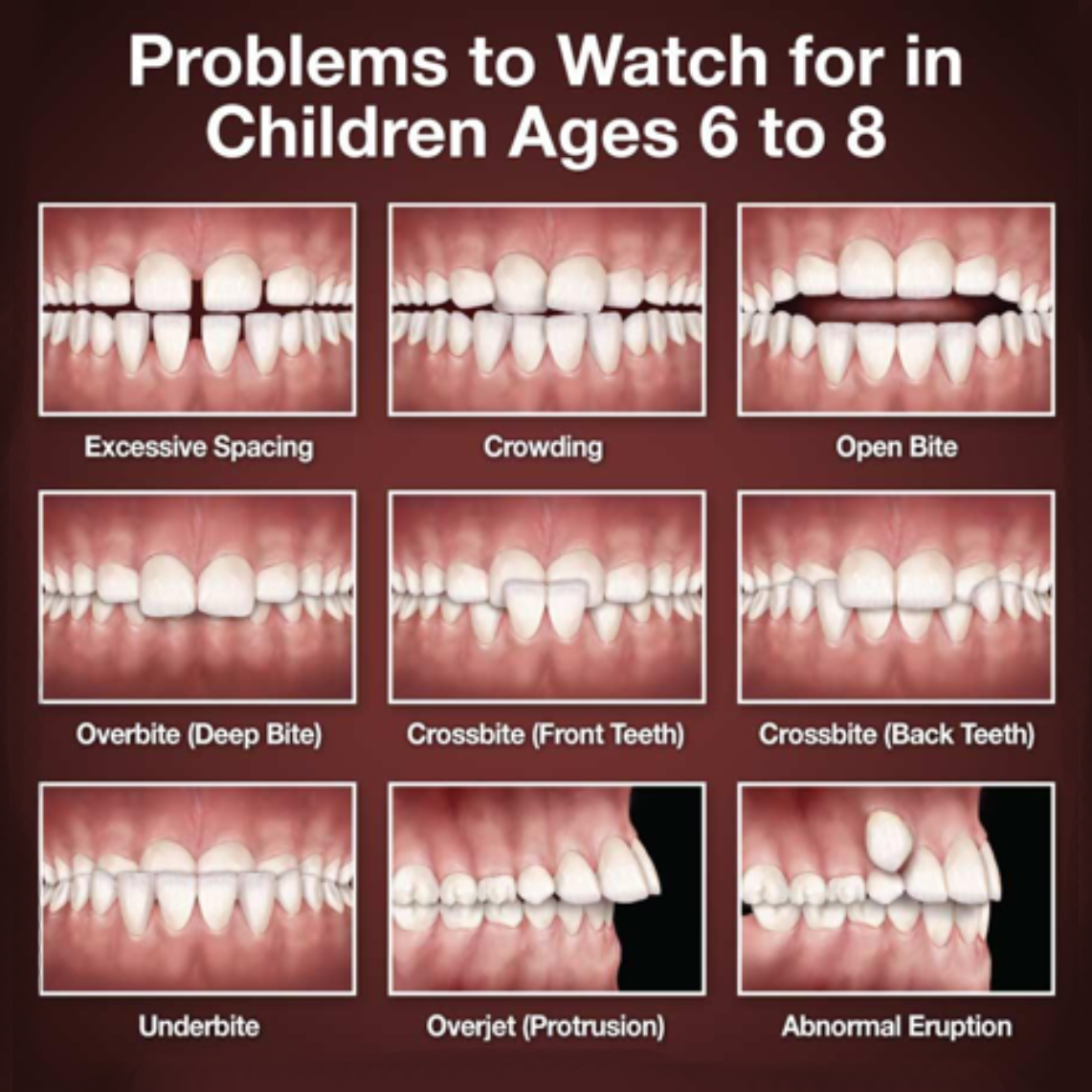
Orthodontic Concerns
By around age 7, most malocclusions have become evident. Interceptive orthodontic treatment around this time can help direct proper tooth positioning and/or jaw growth, eliminating or simplifying the need for later treatment. There are many orthodontic problems that can be detected early and are examples of why a trained professional should evaluate your child during his/her growth and development.
Sports & Your Child's Teeth
If your child is active in sports, we highly recommend a custom-made mouthguard. It is estimated that mouthguards prevent more than 200,000 injuries each year. We can have a mouthguard custom-made specifically for your child using a model of his or her teeth that will offer greater protection than an off-the-shelf model. It's an investment that pays off highly in the form of reduced pain, suffering — and dental expenses down the road! Please ask us about mouthguards at your child's next appointment.
While you may think that some loss of teeth is inevitable as we age, it is actually possible for all of your teeth to last a lifetime. One of the ways you can achieve this goal is to avoid periodontal disease (“peri” – around; “odont” – tooth), which is caused by bacteria that attack the tissues around the teeth. Unfortunately, you may not even realize you have gum disease as the signs and symptoms are not always as apparent to you as they are to a dental professional.
Nearly all people who do not maintain good daily oral hygiene will develop gingivitis. If left untreated, this bacterial gum infection can progress from gingivitis (“gingival” – gum; “itis” – inflammation) to periodontitis, which results in bone loss around your teeth. As the bone tissue is lost, the gum tissues detach from the teeth and form little pockets that provide an even better place for bacteria to live — where your brush and floss can't reach. As periodontal disease advances leading to more bone loss, tooth loss can result. Part of this has to do with genetics, as periodontal disease tends to run in families. The good news is that periodontal disease can be controlled, even at more advanced stages.